Publications
Reports
The Economic Rationale for Investing in School Meal Programs for Canada: multi-sectoral impacts from comparable high-income countries
By Ruetz, A.T., Edwards, G., Zhang, F. (Ruetz Consulting, October 2023)
Suggested citation: Ruetz, A.T., Edwards, G., Zhang, F. (2023, October 26). The Economic Rationale for Investing in School Meal Program for Canada: multi-sectoral impacts from comparable high-income countries. A Report Prepared by Ruetz Consulting for the Government of Canada, funded by the Arrell Family Foundation. Available at: https://amberleyruetz.ca/assets/uploads/ruetz-consulting_the-economic-rationale-for-investing-in-school-meal-programs-for-canada.pdf
Comprehensive, Integrated Food and Nutrition Programs in Canadian Schools: A Healthy and Sustainable Approach
By Jess Haines and Amberley T Ruetz (Arrell Food Institute, March 2020)
Jess Haines & Amberley T Ruetz
Arrell Food Institute
Publication year: 2020
Abstract
Eating a healthy diet is critically important, especially for children; it leads to short- and long-term health benefits, increases academic performance, and sets up healthy habits for a lifetime. To ensure all Canadian children are receiving these benefits, a universal and comprehensive National School Food Program is a critical step in providing children with healthy, safe food, reducing child and household food insecurity, teaching food skills, and supporting local food systems.
Recommendations
Click here for the two-page Policy Brief. In summary, our recommendations include:
- Nutrition education should be required in K–12 curricula, with a focus on hands-on food literacy, school policies, and meal programs.
- Any development of a national level program to promote healthy eating habits among children and teens should be integrated and comprehensive, meaning:
- healthy eating habits are included in the curricula, and also modelled and supported through policies and hands-on food skills programs in schools;
- local communities, school administrations and indigenous communities continue to have autonomy; and
- universally-available to all students
- sufficiently funded and supported with the necessary physical infrastructure and human resources.
- Policy actions can contribute to this goal, including:
- Convening cross-ministry working groups to provide comprehensive support to school food programs;
- harmonized nutrition standards that are fully implemented, monitored and regularly evaluated;
- enhancing current curriculum and training.
Op-eds
Universal School Meals: Putting Child Health Back on the Front Foot
By (UNICEF Canada, December 2022)
A national school food program for all: Towards a social policy legacy for Canada
By Amberley Ruetz, Alicia Martin and Eric Ng (Canadian Centre for Policy Alternatives, July 2022)
Canada’s pandemic recovery urgently needs a national school meal program
By Amberley Ruetz (The Conversation Canada, January 2022)
Feed the children: Canada needs to sign on to Global School Meals Coalition
By Amberley Ruetz & Debbie Field (The Hill Times, September 2021)
School gardens and kitchens could grow with Ontario’s proposed food literacy act
By Alicia Martin and Amberley Ruetz (Conversation Canada, May 2021)
Ontario's Food Literacy for Students Act (Bill 216) aims to make food literacy mandatory for all Ontario students in grades 1-12 to "ensure that students are given opportunities to grow food, prepare food and learn about local foods."
A National School Food Program should be part of Ottawa's Stimulus Package
By Amberley Ruetz, Evan Fraser, John Smithers and Jess Haines (Policy Options, October 2020)
Providing healthy school food would support all families, and a buy-Canada focus would help the agriculture, food service, and construction sectors.
Time for Action: Critical next steps to create a National School Food Program
By Jess Haines and Amberley Ruetz (The Hill Times, March 2020)
National School Food Program a short-term opportunity for jobs creation and economic growth
By Amberley Ruetz and Dr. Evan Fraser (Canadian Science Policy Centre, March 2019)
The implementation of a National School Food Program in Canada could create as many as 207,700 jobs and contribute $4.8 Billion in domestic food purchases by 2029.
Federal budget pledges a Canadian school food program but recipe requires funding
By Amberley Ruetz and Dr. Sara Kirk (Conversation Canada, March 2019)
“Food at school can improve children’s health and academic outcomes while creating economic opportunities for local, sustainable agriculture”.
‘Farm-to-school’ Movement Takes Root in Canada
By Amberley Ruetz and Dr. John Smithers (Conversation Canada, August 2018)
A “farm-to-school” movement is growing fast across Canada but there has been little research to evaluate their potential to support local food systems and economic development. My OMAFRA-funded research will examine the farm-to-school phenomenon as an agri-food value chain and assess how these programs might evolve to expand the scope and sustainability of local food systems in Ontario.
Article republished by Toronto.com; the Weather Network, the Hamilton Spectator, York Region News, BizCommunity, and the University of Guelph News.
How to make a National School Food Program happen
By Amberley Ruetz and Dr. Sara Kirk (Conversation Canada, August 2018)
The article gained considerable media attention, with over 24+ interviews on CBC morning shows across the country. The article was republished by the Huffington Post Canada, the Huffington Post, the Winnipeg Free Press, the Halifax Chronicle Herald, the University of Dalhousie News, the University of Guelph News and the Huntsville Doppler.
Journal Papers
Scaling up ‘local’ in school food programs: Exploring intermediated farm-to-school procurement in Ontario.
By Ruetz, A.T. & Smithers, J. (The Journal of Rural and Community Development, July 2023)
School Food Programming across Canada during the COVID 19 Pandemic: Program Reach and Modalities
By Suvadra Datta Gupta, Rachel Engler-Stringer, Amberley T Ruetz & Mary L McKenna (Journal of Hunger & Environmental Nutrition, July 2022)
Suvadra Datta Gupta, Rachel Engler-Stringer, Amberley T Ruetz & Mary L McKenna (2022). School Food Programming across Canada during the COVID 19 Pandemic: Program Reach and Modalities, Journal of Hunger & Environmental Nutrition, DOI: 10.1080/19320248.2022.2105185
Publication year: 2022
Abstract
In 2020, after the COVID-19 pandemic resulted in widespread school closures and a consequent pause in school food programs (SFP), stakeholder groups soon found alternate methods for delivering meals and snacks to students. This paper examines the breadth of school food programming in Canada during the pandemic. SFPs collectively offered meals (breakfast was most frequent), food boxes, and gift cards and average weekly distributions were over 10,000 meals. In most cases, the programs provided enough food/coupons to feed multiple or all household members. Almost half the programs received funding from provincial/territorial governments and around two-thirds received charitable contributions.
COVID-19 School Re-Opening Plans: Rolling Back School Food Programming in Canada?
By Mary E Coulas, Amberley T Ruetz, Mariam R Ismail, Lindsay Goodridge, Sterling Stutz & Rachel Engler-Stringer (Frontiers in Communication, April 2022)
Mary E Coulas, Amberley T Ruetz, Mariam R Ismail, Lindsay Goodridge, Sterling Stutz & Rachel Engler-Stringer
Frontiers in Communication
Publication year: 2022
Abstract
At the beginning of 2020 national school food programs reached more children than any time in history making school food programs the most extensive form of social safety nets in the world. Looking to Canada, school food programs across the country serve more than 1 million students and provide multifaceted benefits including access to healthy fresh food choices, improving learning capacities, promoting nutritional awareness, assisting food-insecure households, and promoting local food procurement.
However, since the beginning of the SARS-Cov 2 (COVID-19) pandemic these programs have faced operational challenges resulting in many rolling back their operations while food insecurity rates in Canada have increased dramatically. Framed as a Canadian case study analysis, this paper considers the discursive effects of provincial and territorial school reopening plans and the material consequences felt by SFPs.
Specifically, this paper considers the reach, effectiveness, adoption, implementation, and maintenance of provincial and territorial school food programs within the broader conceptualization of ecological public health to consider if these programs were enabled or constrained by school reopening plans. The authors conducted a policy analysis of 57 primary and 164 supportive school reopening documents developed between April 2020 and September 2021.
It was found that provincial and territorial school reopening plans primarily focused on measures to limit infectious disease transmission while food discussed in broad terms demonstrated policy makers’ limited awareness of the important role of school food programs and support required to maintain them. In turn, two key observations were made: 1) government school reopening plans have overlooked the benefits of school food programs in Canada, and 2) school reopening plan designers missed opportunities to improve school food programs.
This paper argues a thorough understanding of the impacts to school food programs by provincial and territorial COVID-19 public health guidelines is needed for politicians, policymakers, and school food practitioners to support the short- and long-term capacity of these programs and to ensure food insecurity and nutritional health issues in Canada continue to be on the political agenda.
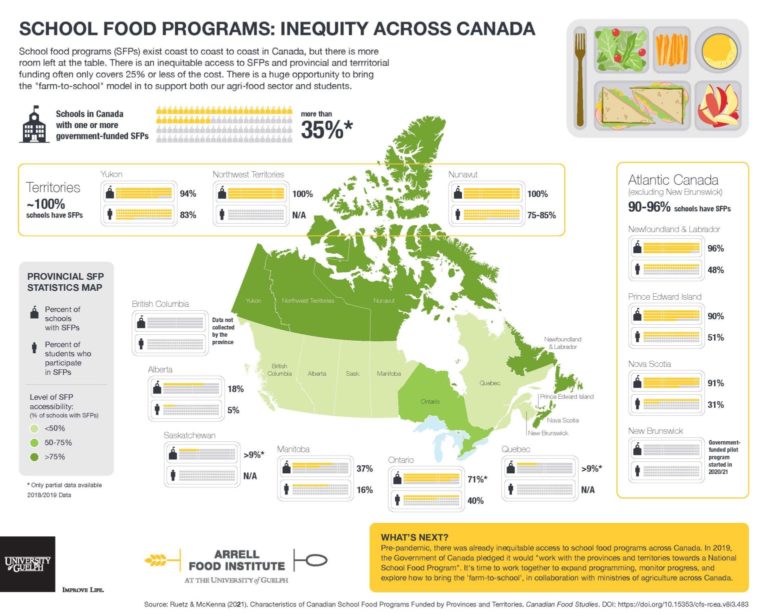
Characteristics of Canadian school food programs funded by provinces and territories
By Amberley T. Ruetz & Mary L. McKenna (Journal of Hunger & Environmental Nutrition, October 2021)
Amberley T. Ruetz & Mary L. McKenna (2021). Characteristics of Canadian school food programs funded by provinces and territories. Canadian Food Studies, Volume 8, Issue 3. https://canadianfoodstudies.uwaterloo.ca/index.php/cfs/article/view/483
Publication year: 2021
Abstract
Given the complex administration of school food programs (SFPs) in Canada and recent federal interest, this research systematically examined provincial and territorial funded SFPs during the 2018/19 school year. Relevant literature and the RE-AIM Framework, a planning and evaluation tool developed by Glasgow et al. (1999), informed the development of an electronic survey sent to program leads in provinces and territories to assess SFP Reach, Effectiveness, Adoption, Implementation, and Maintenance. Results from 17 programs indicate considerable administrative and program variability across Canada.
Collectively, provinces and territories contributed over $93 million which partially funded a minimum of 35% of JK-12 schools to provide free breakfasts, snacks, and/or lunches to a minimum of 1,018,323 or 21% of students in Canada (based on limited data in some jurisdictions). The majority of provinces and territories partner with one or more non-governmental organization (NGO) and rely heavily on NGO staff and volunteers. Program demand often exceeds supply, and program monitoring is inconsistent.
This research–which provides much-needed, updated information on SFPs–highlights the need to explore the complexity of the topic further and helps inform discussions about SFP administration and characteristics, specifically program mandates, student reach and universality, program sustainability and resources, and monitoring. Opportunities exist for (1) a closer examination of varied and promising organizational practices, (2) enhanced collaboration and knowledge sharing, and (3) harmonization of key metrics, all of which would assist with developing the National School Food Program proposed in the 2019 federal budget.